Zeshancheng-1202
 Welcome to call for consultation on customization.
Welcome to call for consultation on customization.
product details
Zeshancheng-1202 Introduction
Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218) is a thermoplastic polyimide micro-powder that exhibits excellent solubility, along with low thermal expansion coefficient, low dielectric constant, high glass transition temperature, low density, high toughness, and low water absorption rate.
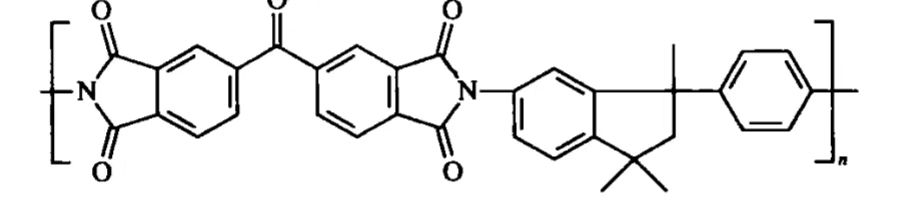
characteristic :
At room temperature, Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218) micro powder is fully soluble in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC), N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), m-cresol, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), γ-butyrolactone (GBL), benzyl ether (Anisole), 1,4-dioxane, carbon tetrachloride, dichloromethane, and chloroform, with a solid content of up to 40%. It is insoluble in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, butanone, and toluene.
Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218) micro-powder, tested by DSC, exhibits a glass transition temperature of approximately 327°C. The compression-molded profile of Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218), tested by DMA, shows a glass transition temperature of about 346°C. Notably, its elastic modulus remains above 1.0GPa even at 320°C.
Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218) exhibits a refractive index as low as 1.639, from which the calculated dielectric constant is approximately 2.70.
The toughness of the thermosetting resin cured with Zeshancheng-1202 (Matrimid 5218) micro-powder toughening modifier—such as special epoxy, bismaleimide, and cyanate ester resins—is 2 to 4 times higher than that of the unmodified version.
Material application:
A, serves as a high-performance thermoplastic matrix resin with high-temperature resistance and toughness
B, for toughening modification of thermosetting matrix resin
C, used for manufacturing high-temperature resistant insulating coatings and gas separation layers
D, for manufacturing components or tooling fixtures for high-temperature applications


